
16 Ground Wave Propagation Follows contour of the earth Can propagate considerable distances Frequencies up to 2 MHz Example AM radio 17.

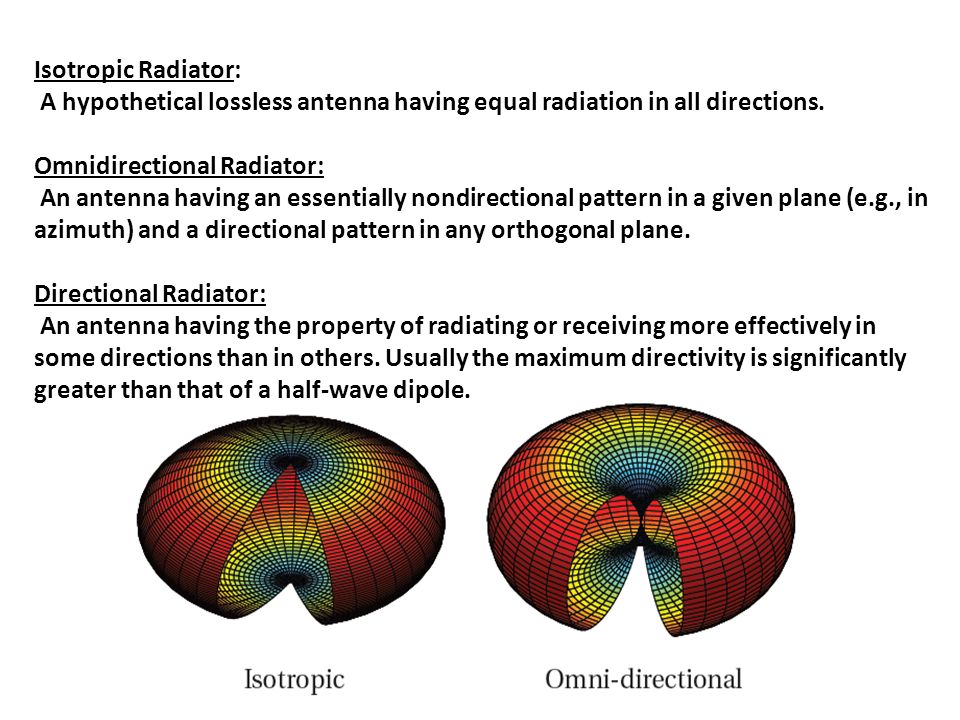
15 Propagation Modes Ground-wave propagation Sky-wave propagation Line-of-sight propagation 16. 14 Dipole Antenna Power radiated Azimuth 15. 13 Types of Antennas Isotropic antenna Idealized Radiates power equally in all directions Omnidirectional Dipole antennas Half-wave dipole antenna Hertz antenna Quarter-wave vertical antenna Marconi antenna Parabolic Reflective Antenna 14. 11 Polarization Vertically Polarized Antenna Electric field is perpendicular to the Earths surface e.g., Broadcast tower for AM radio, whip antenna on an automobile Horizontally Polarized Antenna Electric field is parallel to the Earths surface e.g., Television transmission (U.S.) Circular Polarized Antenna Wave radiates energy in both the horizontal and vertical planes and all planes in between 12. 10 Polarization Defined as the orientation of the electric field (E-plane) of an electromagnetic wave Types of polarization Linear Horizontal Vertical Circular 11. 9 Antenna Gain (cont.) An antenna with a G = 3dB improves over the isotropic antenna in that direction by 3dB or a factor of 2 10. 8 Antenna Gain (cont.) Relationship between antenna gain and effective area G antenna gain Ae effective area f carrier frequency c speed of light ( 3 x 108 m/s) carrier wavelength 9. 7 Antenna Gain Antenna gain Power output, in a particular direction, compared to that produced in any direction by an isotropic antenna Effective area Related to physical size and shape of the antenna 8.

6 Radiation Patterns (cont.) Beam width (or half-power beam width) Measure of directivity of antenna 7. 5 Radiation Patterns Radiation pattern Graphical representation of radiation properties of an antenna Depicted as a two-dimensional cross section Reception pattern Receiving antennas equivalent to radiation pattern 6. 4 Reciprocity In general, the various properties of an antenna apply equally regardless of whether it is used for transmitting or receiving Transmission/reception efficiency Gain Current and voltage distribution Impedance 5. 3 Fundamental Antenna Concepts Reciprocity Radiation Patterns Isotropic Radiator Gain Polarization 4. 2 Introduction An antenna is a transducer that converts radio frequency electric current to electromagnetic waves that are radiated into space In two-way communication, the same antenna can be used for transmission and reception 3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
